-
 Call Now ! +94 11 431 1111
Call Now ! +94 11 431 1111 -
 Email Now [email protected]
Email Now [email protected]
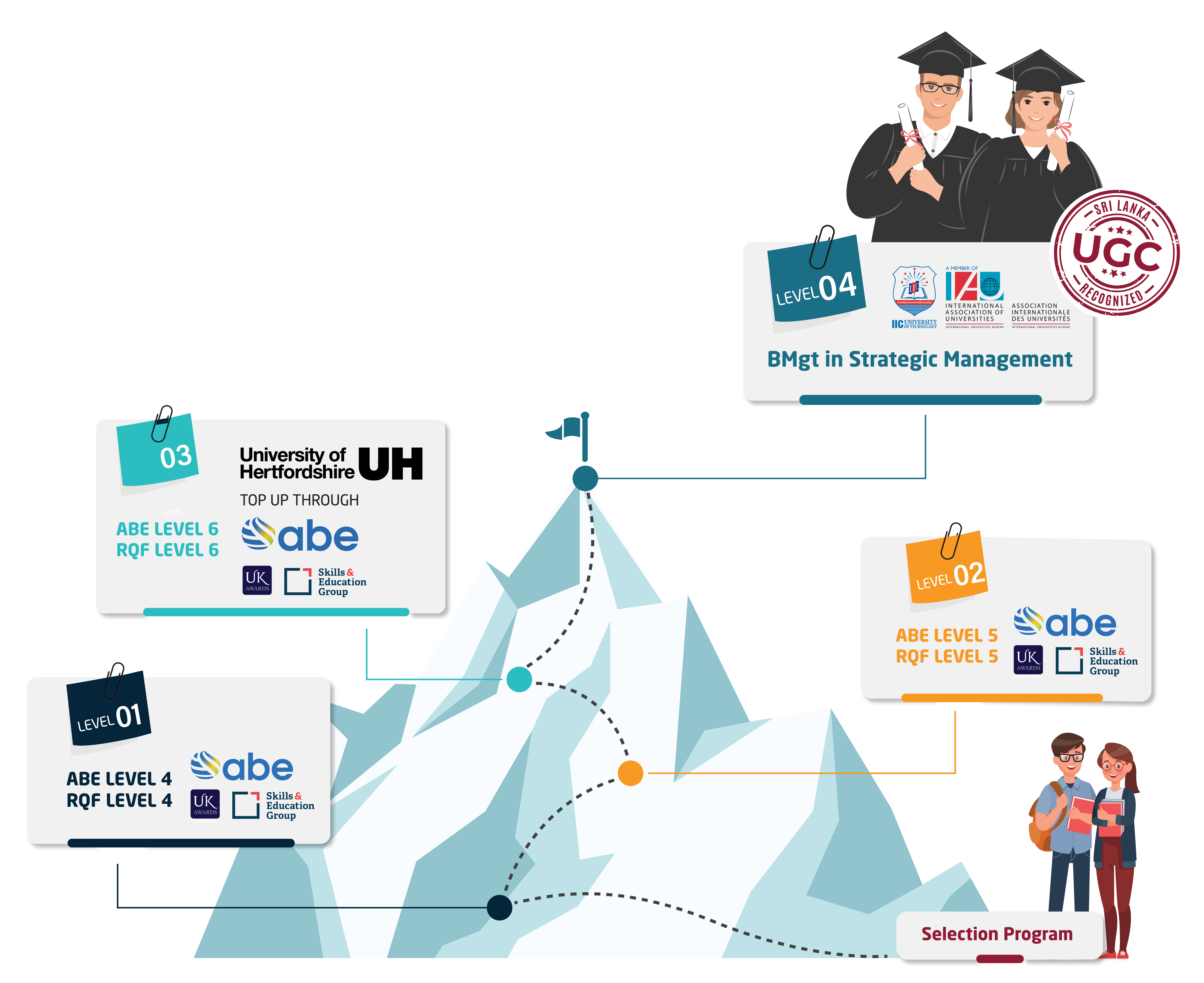
Strategic Management Graduate Degree (MPhil+BMgt) in Sri Lanka
Leads to PhD in Strategic Management



In this unit, You will analyse the impact of increasingly dynamic business environments and increasingly volatile markets on an organization’s ability to compete successfully using a range of relevant tools and frameworks.
This unit develops an understanding of the principles of business and the different legal formations by which an organization can operate. As an organization grows and evolves, the need for different structures will take effect. You will also be introduced to the common organization structures, whilst developing an appreciation for contemporary structures, as both external influences impact upon an organization requiring a more efficient and effective approach to delivering products or services. You will be developing skills in evaluation of both quantitative and qualitative data to make judgements about the types of structures suitable for different organizations and the sectors in which they operate.
This unit introduces you to the key skills, behaviours, and attitudes you need to demonstrate in order to be ‘employable’, and how to develop them if they are missing, through self-development and/or other learning, development and improvement opportunities. It provides guidance on how to integrate this information to the documents required for job applications, and how to present these skills at an interview. It goes on to show how demonstrating employability skills can help enable a smooth transition into work by establishing you in your new job role and as part of a team.
This unit is designed to enable you to gain a knowledge and understanding of accounting principles, processes, and concepts that can be applied in a general management context. These principles, processes, and concepts are key in the understanding of how a business operates and what ultimately makes it successful.

In Introduction to Entrepreneurship, you will learn key success factors for enterprises and how to apply these to successfully innovate, develop, and grow a business. Key business strategies, business development, and the management of the enterprise through the business cycle will be explored.

The focus of the Quantitative Methods syllabus is to:

This unit expands the basic theory of project management into a practical, operational context and integrates all the fundamental tools and techniques required to manage business projects successfully.

This unit introduces you to teamwork and the characteristics of effective teams. It will address team member skills and how to build effective working relationships within different types of teams and business structures, including virtual environments.

This foundational qualification serves as an introduction to the broad domain of strategic management. It provides students with a comprehensive overview of the fundamental concepts, theories, and principles in strategic management. The module emphasizes the role of strategic planning in achieving an organization's goals and objectives and guides students through the process of formulating, implementing, and evaluating strategies. Topics include the strategic management process, internal and external environmental scanning, strategy formulation, strategic choice, and strategy implementation. Students will gain a strong grasp of these concepts and develop analytical skills to make strategic decisions that drive sustainable competitive advantage.



Examining how people's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by social interactions and group dynamics can be valuable for developing effective organizational strategies.


This module will explore the ancient technologies and engineering practices of Sri Lanka, dating back to over 2000 years ago. Students will learn about the construction techniques, materials, and innovations used in the creation of ancient structures, such as irrigation systems, temples, and monuments. The module will also cover the cultural and historical context surrounding the development of these technologies, including the role of religion and politics.

This unit aims to cover the main areas in regard to Research Methodology including the terminology, concepts, conventions and research methods where students will be given a practical experience on the systematic procedures by which research is conducted, enabling them to critically identify, describe and formulate conclusions based on hypothesis testing while evaluating a study’s overall validity and accuracy.

The Voluntary module is designed to explore the concept of voluntary service in the context of strategic management. This module will examine how voluntary service can be utilized as a strategic tool for achieving organizational goals and objectives.

As a result of studying this unit, you should be able to appraise the issue of innovation as it falls within, and relates to, a range of key business functions and disciplines. You should additionally be able to form a holistic view of the drivers and effects of innovation on the business enterprise, and to develop an awareness of the need to innovate.
As a result of studying this unit, you should be able to appraise the issue of innovation as it falls within, and relates to, a range of key business functions and disciplines. You should additionally be able to form a holistic view of the drivers and effects of innovation on the business enterprise, and to develop an awareness of the need to innovate.
The focus of Effective Financial Management is the management of financial resources in a business. It addresses the applied techniques that managers need in order to take financial decisions in a business. It also addresses the critical and theoretical knowledge and skills that managers need to take financial management responsibilities.
This unit is aimed at developing a strong working understanding of economic theory and principles in the everchanging and dynamic international economic marketplace. When a firm decides to engage in international trade, it has different options. The aim of this unit is to make you aware of the relevance of each method of entry with the analysis of case histories.

In this unit, you will explore different stakeholders in depth, analysing their potential impact and influence, in order to develop relevant relationship management strategies that will enable organisations to overcome threats, take advantage of opportunities, achieve their objectives and protect their brand.
This unit is designed to provide you with the theoretical, practical, and technical knowledge and understanding to build a capability to identify, define, analyse, and interpret data from a broad range of sources to support critical business decisions in a variety of contexts and using a range of methodologies.
Building on the foundational knowledge of Strategic Management I, this module delves into the entrepreneurial aspect of strategic management. This course focuses on the application of strategic management concepts in entrepreneurial contexts, particularly in startups and small businesses. Students will explore how entrepreneurial firms formulate and implement strategies to gain competitive advantage and sustain growth. They will learn to apply entrepreneurial thinking to strategic management problems and gain insights into innovation, opportunity recognition, business model design, and the strategic challenges of growth and scaling. This module offers a blend of theory and practice, preparing students for future entrepreneurial pursuits or roles in dynamic business environments.

This unit focuses upon the leadership principles required to lead an organisation and its stakeholders through strategic change. It explores key leadership models and methodologies and how these can be applied by leaders within organisations. Understanding how these principles support an organisation’s current vision, values and strategic direction is an important aspect covered by this unit.
This unit focuses upon the structure, process and scope of developing and evaluating appropriate business strategies in varied market and organisational contexts. The unit recognises the challenges to strategy and decision makers in the current business environments, taking into account the dynamic and contemporary issues driving strategic thinking in many organisations in pursuit of competitive advantage.
The focus of this unit is on international market development and is designed to help you understand marketing practice from a global perspective. The unit will consider and assess a range of different market entry models and tactics, and consider the implications of increasing globalisation.
This unit will develop your understanding of managerial and organisational principles through considering the role of ethics in business operations, including corporate social responsibility, sustainability and responsible management. You will examine the origins, theory and practice of these closely interconnected issues.
(ABE optional subject) This unit will take you through a step-by-step process that will enable you to identify, analyse and prioritise an organisation’s stakeholders from a strategic perspective, and then to plan, implement and review the stakeholder engagement process in relation to a specific project.
This unit will build on the fundamental principles covered in the Level 4 Project Management unit and enable you to develop knowledge of the advanced principles, practices and techniques vital to the successful leadership and commercial management of complex projects.

This module dives into the realm of transformation management, an essential component of strategic management. This module discusses how organizations manage and respond to significant strategic changes, whether due to industry disruption, competitive shifts, technological advancements, or regulatory changes. Students will explore change management theories and methodologies, the role of leadership in guiding change, and the interplay between strategy and culture during transformations. The course underscores the importance of agility, resilience, and innovation in crafting transformation strategies and prepares students to lead strategic change initiatives effectively.

Strategic Management IV synthesizes the concepts learned in previous modules and introduces more complex topics in strategic management. Students will delve into areas like strategic alliances, mergers and acquisitions, corporate governance, and international strategy. The module discusses the challenges and opportunities of implementing strategies at a global scale, managing strategic partnerships, and leading strategic initiatives in large, complex organizations. By the end of this module, students will have a robust understanding of the complexities of strategic management and the leadership skills needed to implement strategic decisions in diverse, multinational contexts.

The "Strategic System Automation" module is designed for students with prior knowledge in business strategy and basic understanding of information systems. The module focuses on the intersection of business strategy and system automation, explaining how automated systems can contribute to strategic business goals. It covers principles of system automation, cost-benefit analysis, risk assessment, and change management. The course also includes an in-depth look at technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Robotic Process Automation, and Machine Learning, viewed from a strategic perspective. The module concludes with case studies of successful strategic automation initiatives, preparing students for leadership roles in tech-driven business environments.

This field of psychology examines workplace dynamics, employee satisfaction, productivity, and organizational culture, providing insights into strategic human resource management.


This subject focuses on understanding how individuals process information, make decisions, and solve problems, which can inform strategic decision-making processes.


Knowledge of psychometric tools and techniques can aid in strategic talent acquisition, selection, and performance evaluation.

